Glass-Ceramic vs. Zirconia: The Ultimate Guide to Dental Restorative Materials
In the field of modern dental restorations, selecting the right material is critical to the esthetic outcome, functional longevity, and overall patient satisfaction. Dentists, dental laboratories, and dental trading companies (especially partners seeking wholesale dental glass-ceramic blocks and a reliable “dental supplies glass-ceramic supplier”) often face a core question: How do we make the most informed decision between dental glass-ceramic and zirconia? This is not merely a technical consideration; it also involves clinical efficiency, processing costs, and ultimate business value.
As a dental trading company leveraging the robust supply chain advantages of China, ERADENT understands the challenges you face in sourcing and applying dental materials. We are committed to providing high-quality dental zirconia, glass-ceramic, PMMA, Ti-CoCr alloys, milling burs, and more. Our goal is to help you solve practical pain points and enhance your competitive edge. This article will provide an in-depth comparison of “glass-ceramic vs. zirconia”, offering authoritative, practical guidance to help you choose the best glass-ceramic for anterior crowns or the most suitable material for posterior teeth, and answer common questions like, “Is glass-ceramic stronger than zirconia?”
An In-Depth Look at Dental Glass-Ceramics: The Epitome of Esthetics and Precision
Composition and Types of Glass-Ceramics
Glass-ceramics are primarily composed of a glass phase and a crystalline phase, which are precisely controlled to give the material its unique physical and chemical properties.
- Lithium Disilicate Glass-Ceramic: This is the most widely used type of glass-ceramic today, such as the lithium disilicate blocks offered by ERADENT. Its crystalline structure provides excellent translucency and a biaxial flexural strength of up to 500 MPa (ERADENT Glass-Ceramic reaches 637 MPa), making it an ideal dental crown material and “dental veneer material

- Feldspathic Glass-Ceramic: A traditional esthetic restorative material known for its excellent light transmission, but with relatively lower strength. It is primarily used for veneers.
- Leucite-Reinforced Glass-Ceramic: With strength between that of lithium disilicate and feldspathic glass-ceramics, this material offers good esthetics and machinability.
Key Advantages of Glass-Ceramics
- Superior Esthetic Performance (dental esthetic material): The translucency, opalescence, and refractive index of glass-ceramics closely mimic natural tooth enamel, allowing restorations to blend seamlessly into the oral environment for an “invisible” repair. This is crucial for anterior crowns that demand the highest level of esthetics.
- Excellent Bonding Performance: The surface of glass-ceramics can be etched with hydrofluoric acid to create a micro-retentive pattern. A silane coupling agent is then applied to form a strong chemical bond with resin cements, ensuring long-term stable retention of the restoration.
- Low Antagonist Wear: The hardness of glass-ceramics is similar to that of natural enamel, effectively reducing wear on the opposing teeth and protecting the patient’s natural dentition.
- Good Biocompatibility: The material is non-irritating to oral tissues and is unlikely to cause allergic reactions, ensuring patient comfort and health.
- CAD/CAM-Friendly (CAD/CAM glass-ceramic): Suitable for digital milling, enabling precise and efficient fabrication of restorations, meeting the needs of modern “dental lab glass-ceramic solutions”.
Limitations and Indications for Glass-Ceramics
Despite their significant advantages, glass-ceramics have lower strength compared to zirconia and are not suitable for long-span posterior bridges that endure high masticatory forces. Their ideal indications include:
- Anterior single crowns and veneers (“dental veneer material”)
- Inlays and onlays
- Anterior crowns
- Posterior crowns
- Monolithic bridges (3-unit)
- Minor adjustments to tooth color or shape
An In-Depth Look at Dental Zirconia: A Symbol of Strength and Versatility
Zirconia has established an indispensable position in dental restorations due to its exceptionally high strength and toughness, especially for areas subjected to high chewing forces and multi-unit bridges.
Composition and Types of Zirconia
Dental zirconia is typically yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), where varying amounts of yttrium oxide are added to stabilize its crystalline structure.
- Conventional High-Strength Zirconia: Possesses extremely high flexural strength (often exceeding 1000 MPa) but has poor translucency. It is mainly used for posterior restorations and bridges.
- High-Translucency (HT) Zirconia: By adjusting grain size and yttria content, translucency is improved. This allows it to be used in the anterior region while maintaining sufficient strength.
- Multilayer Zirconia: Mimics the natural gradient of color and translucency from the cervical to the incisal edge of a tooth, further enhancing the esthetic performance of zirconia.
Key Advantages of Zirconia
- Exceptional Strength and Toughness: Zirconia can withstand immense chewing forces, making it an ideal dental crown material and choice for “dental bridges”, particularly in the posterior region and for long-span restorations.
- Excellent Biocompatibility: Similar to glass-ceramics, zirconia exhibits outstanding biocompatibility.
- Corrosion Resistance: It remains stable in the complex oral environment and is resistant to corrosion.
- Minimal Tooth Preparation Required: Zirconia can provide adequate structural support even with limited tooth preparation.
Limitations and Indications for Zirconia
The primary limitation of conventional zirconia is its esthetic performance, although this is being progressively addressed with the development of high-translucency and multilayer zirconia. Its main indications include:
- Posterior single crowns and bridges (“dental crown material”)
- Long-span bridges
- Implant abutments
- Restoration of large defects after endodontic treatment
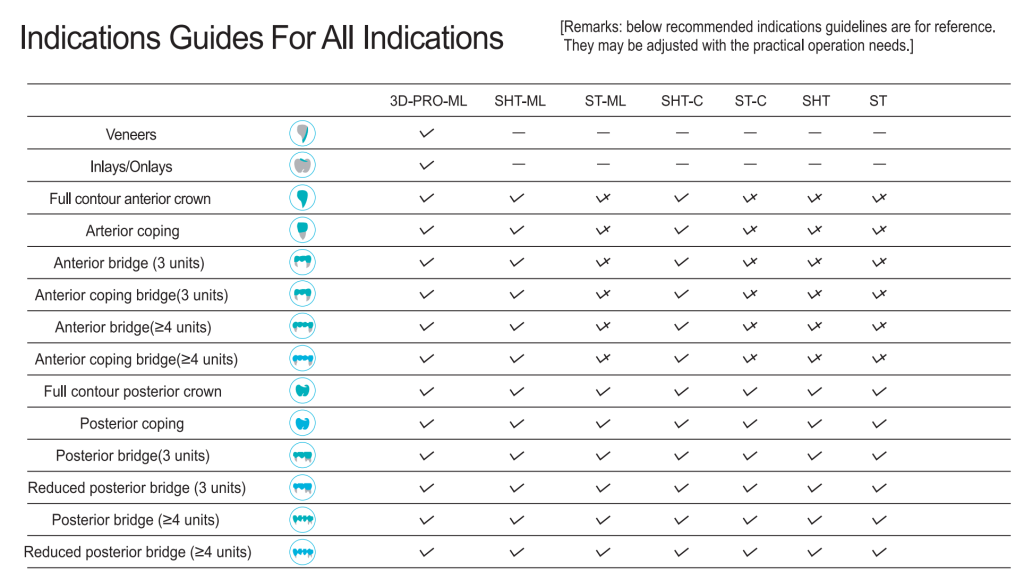
Glass-Ceramic vs. Zirconia: A Multi-Dimensional Comparison for Decision Support
When choosing between dental glass-ceramic and zirconia, a comprehensive evaluation across multiple dimensions is necessary to ensure the best restorative outcome and long-term patient satisfaction.
Esthetic Performance: Translucency and Color Matching
|
Feature Dimension
|
Glass-Ceramic (e.g., ERADENT Glass-Ceramic)
|
Zirconia (Conventional/HT/Multilayer)
|
Decision-Making Consideration
|
|
Translucency
|
Highly translucent, similar to natural teeth.
|
Conventional is opaque; HT zirconia is improved.
|
For high-demand anterior esthetics, glass-ceramic is superior.
|
|
Color Match
|
Can be internally characterized and externally stained for a natural look.
|
Conventional has a monolithic color; HT and multilayer enhance esthetics.
|
For ultimate esthetic results, glass-ceramic is the first choice.
|
|
Esthetic Outcome
|
Excellent, especially as a “dental esthetic material”.
|
Good to excellent, but still struggles to match the natural vitality of glass-ceramics.
|
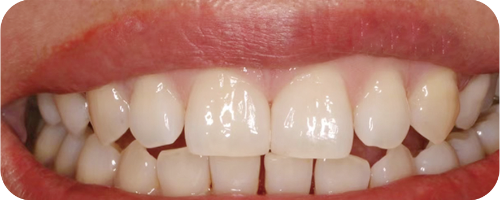
Application cases of anterior glass-ceramic crowns
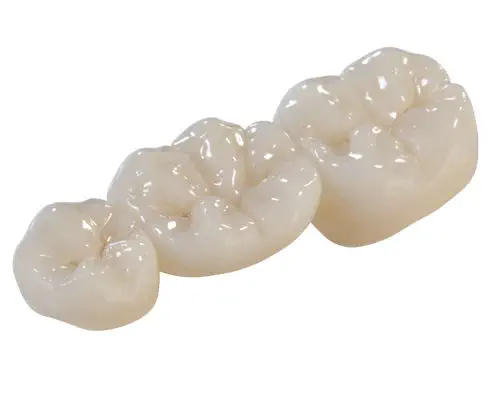
Application cases of zirconia crowns for posterior teeth
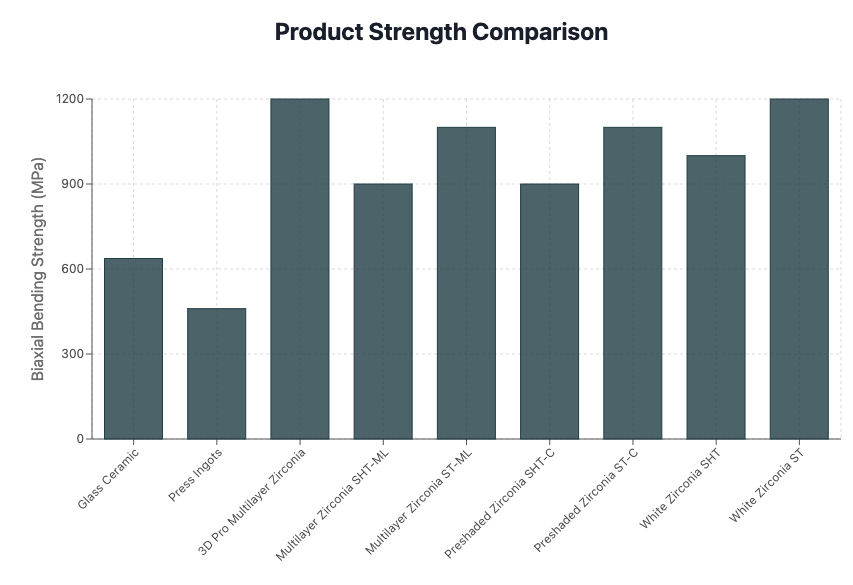
Strength and Durability: Flexural Strength and Fracture Toughness
|
Feature Dimension
|
Glass-Ceramic (e.g., ERADENT Glass-Ceramic)
|
Zirconia
|
Decision-Making Consideration
|
|
Flexural Strength
|
Average 637 MPa (ERADENT CAD/CAM Glass-Ceramic)
|
600–1200+ MPa
|
For posterior regions or long-span bridges, zirconia is superior.
|
|
Fracture Toughness
|
Lower, more prone to brittle fracture.
|
Higher, more resistant to fracture.
|
Bonding and Retention: Cement Choice and Surface Treatment
- Glass-Ceramic: Requires hydrofluoric acid etching (typically for 20 seconds) to create a micro-retentive surface, followed by the application of a silane coupling agent. A light-cure or dual-cure resin cement is then used. The ERADENT glass-ceramic product manual provides detailed crystallization curves and bonding instructions to ensure optimal results.
- Zirconia: The surface is relatively inert. It typically requires sandblasting (with 50-micron aluminum oxide at 0.2 MPa pressure) to increase mechanical retention. A dedicated zirconia primer (containing a monomer like MDP) should be used, followed by a resin cement or resin-modified glass ionomer cement.
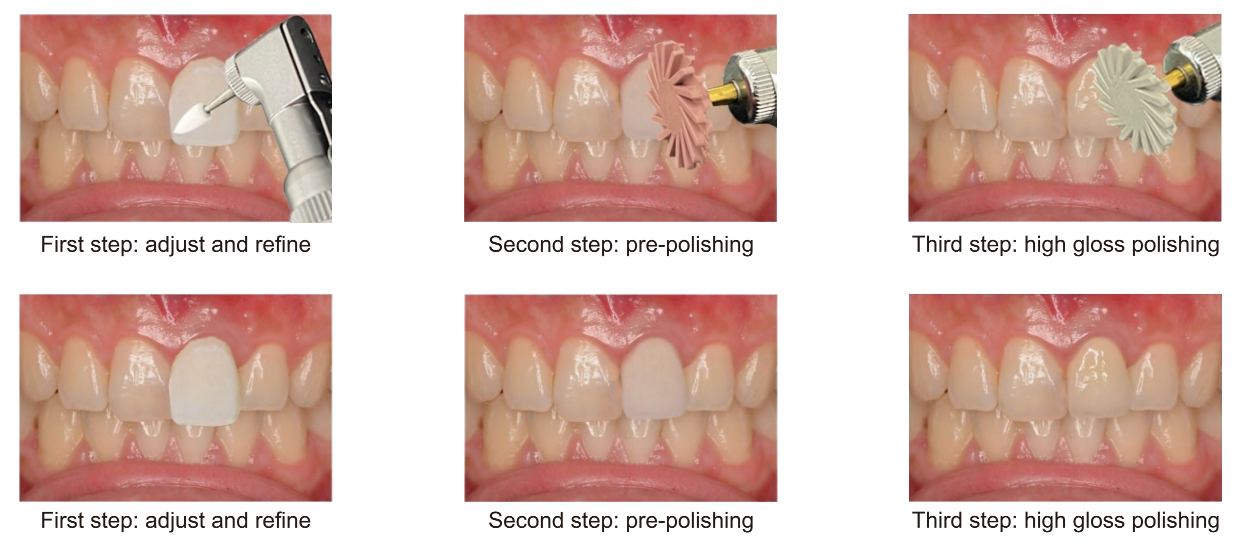
Common Question: How to polish dental glass-ceramic?
Answer: Polishing glass-ceramics is key to ensuring esthetics and reducing wear on opposing teeth. After firing, the restoration is typically finished with fine diamond burs. This is followed by a multi-step polishing process using specialized polishing pastes and brushes until a high-gloss surface is achieved.
CAD/CAM Processing Workflow Comparison
The digital processing workflows for CAD/CAM glass-ceramic and zirconia have different key steps.
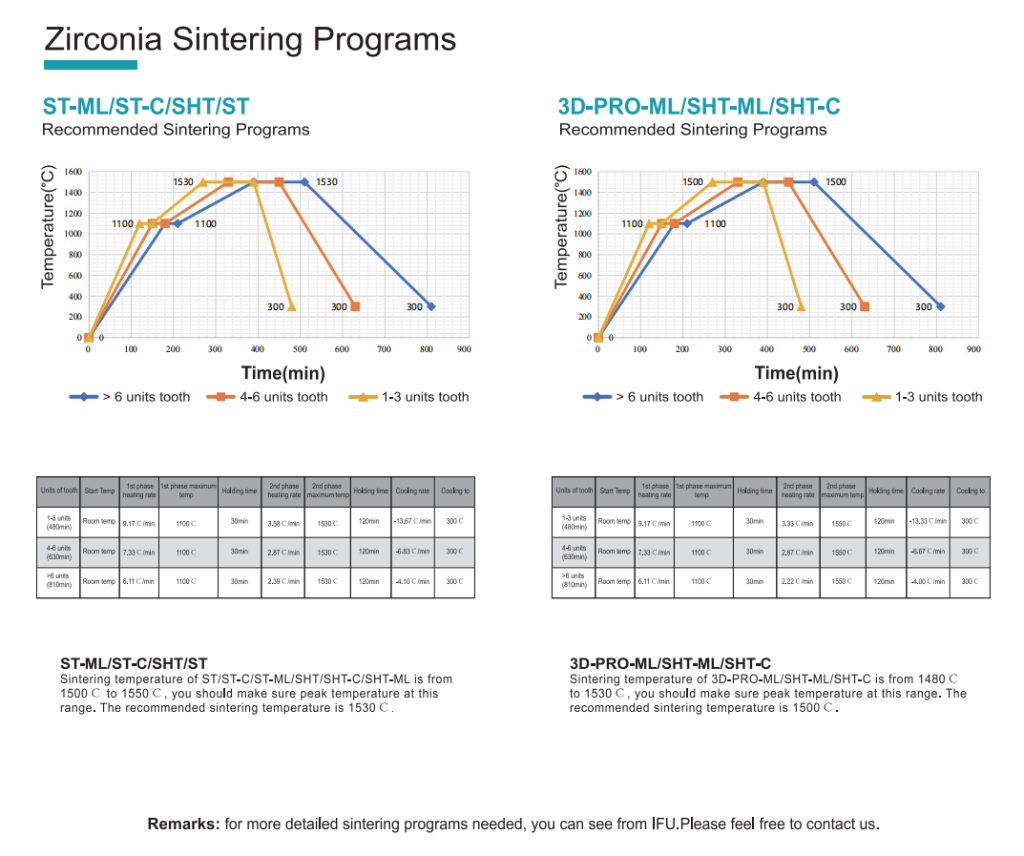
- Glass-Ceramic: Usually processed via wet milling. After milling, it must undergo a crystallization firing process (the crystallization temperature for ERADENT glass-ceramic is between 840–850°C, with a detailed dental glass-ceramic firing schedule provided). This firing step is crucial for developing the material’s final strength and esthetic properties.
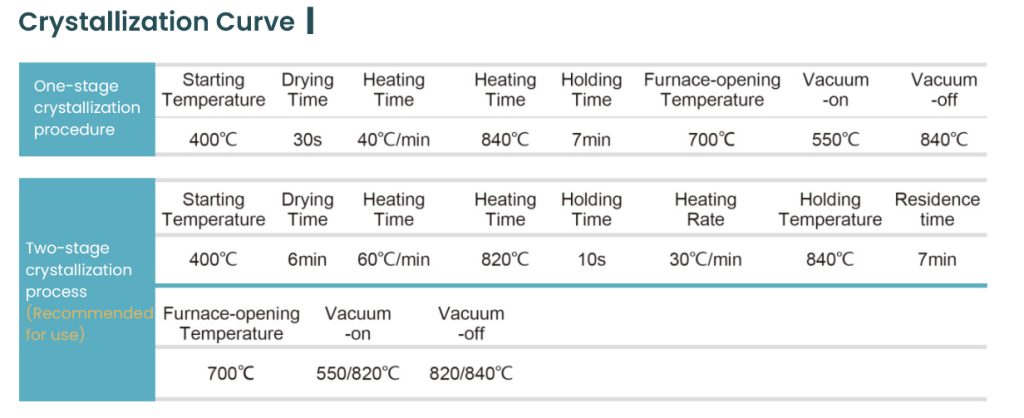
- Zirconia: Typically processed via dry milling. After milling, it requires a high-temperature sintering (densification) process, with temperatures reaching around 1500°C.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
- Cost: The final cost is influenced by material costs, processing time, and remake rates. As one of the leading “dental glass-ceramic manufacturers in China”, ERADENT can provide a competitive dental glass-ceramic price list for distributors and “wholesale dental glass-ceramic blocks”, helping clients optimize their procurement costs.
- Longevity: How long do glass-ceramic crowns last? With proper clinical protocols and good maintenance, both glass-ceramic and zirconia restorations can achieve long-term success. Clinical studies show that both materials have high 10-year success rates, but the actual lifespan is affected by factors such as the patient’s oral hygiene, occlusal forces, and the clinician’s technique.
Clinical Decision-Making: When to Choose Which Material?
Considerations for Anterior vs. Posterior Restorations
- Anterior Restorations: When esthetics are the top priority, such as for the best glass-ceramic for anterior crowns and “dental veneer material”, glass-ceramic is the preferred choice due to its superior translucency and natural appearance.
- Posterior Restorations: When strength and fracture resistance are the primary requirements, especially in the high-stress molar region or for “dental bridges”, zirconia is the superior option.
Single Crowns vs. Multi-Unit Bridges
- Single Crowns: Both glass-ceramic and zirconia can be chosen, depending on the location and esthetic demands.
- Multi-Unit Bridges: Zirconia is the ideal material for multi-unit bridges due to its high strength and fracture resistance. The glass-ceramic vs. zirconia for dental bridges comparison clearly shows that glass-ceramics are only suitable for short-span bridges or those in very high-esthetic demand anterior areas.
Applications for Implant-Supported Restorations
Patient Factors and Clinician Preference
- Patient’s Esthetic Expectations: Clearly understand the patient’s desire for esthetics.
- Oral Habits: Patients with bruxism or clenching habits may require a higher-strength material.
- Budget: Consider the patient’s financial capacity.
- Clinician’s Proficiency: The clinician’s familiarity with the processing and bonding protocols for different materials.
The ERADENT Advantage: Your Reliable Dental Materials Partner
- China Supply Chain Advantage: Leveraging robust domestic manufacturing capabilities, we offer high-performance, cost-effective wholesale dental glass-ceramic blocks and serve as a dependable “dental supplies glass-ceramic supplier”.
- Strict Quality Control: Our glass-ceramic products are FDA and ISO certified, ensuring they meet international standards. ERADENT glass-ceramic blocks feature a uniform surface, consistent color, and are free from impurities and foreign objects, with a biaxial flexural strength of up to 637 MPa.
- OEM & ODM Services: We accept private label dental glass-ceramic orders to meet your unique branding requirements.
- Flexible Shipping Methods: We offer a variety of shipping solutions to help clients save on taxes and duties.
- Comprehensive After-Sales Service: We provide training, professional full-process support, inquiry handling, sample preparation, order processing, shipping and documentation support, and 7/24 rapid response via WhatsApp.
Conclusion: Personalized Choices for Outstanding Restorations
In the choice between “glass-ceramic vs. zirconia”, there is no single “best” material—only the material that is most suitable for a specific clinical situation and the patient’s needs. Dentists must consider the restoration site, esthetic demands, occlusal forces, amount of tooth preparation, and patient expectations. Dental labs must balance processing efficiency, material cost, and the quality of the final restoration. Dental trading companies, in turn, focus on market competitiveness, supply chain reliability, and customer service.
ERADENT is dedicated to being your trusted partner. Our dental glass-ceramic products, with their excellent esthetics, reliable strength, and ease of processing, provide powerful support for your clinical practice and business growth. If you are seeking high-quality CAD/CAM glass-ceramic solutions or wish to learn more about enhancing your product competitiveness, contact us on WhatsApp now to get our dental glass-ceramic price list for distributors. We look forward to working with you to create a brilliant future in dental restorations!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How does ERADENT’s glass-ceramic differ from other brands on the market?
A1: ERADENT’s glass-ceramics (like our lithium disilicate) are manufactured using high-quality raw materials and a refined process, delivering esthetics, high strength (up to 637 MPa), and excellent millability comparable to leading international brands. We focus on providing cost-effective wholesale dental glass-ceramic blocks and customized services to meet diverse procurement needs.
Q2: Is glass-ceramic stronger than zirconia?
A2: Generally, zirconia has a higher flexural strength than glass-ceramic. The average biaxial flexural strength of ERADENT glass-ceramic is 637 MPa, while the strength of zirconia is typically in the 800-1200 MPa range or even higher. Therefore, zirconia is the better choice for high-stress posterior areas or long-span bridges, whereas glass-ceramic excels in anterior regions where esthetics are paramount.
Q3: How long do glass-ceramic crowns last?
A3: With correct clinical procedures, proper bonding protocols, and good oral hygiene from the patient, glass-ceramic crowns can often last for 10 years or more. Regular check-ups and maintenance are key to extending their service life.
Q4: Can glass-ceramic be stained?
A4: Yes, glass-ceramics can be custom-stained and glazed to achieve a perfect color match with the patient’s natural teeth. ERADENT glass-ceramic products are available in a variety of shades and translucency levels and support further characterization for personalized esthetics.
Q5: Does ERADENT offer private label dental glass-ceramic services?
A5: Yes, ERADENT provides OEM & ODM services and supports private label dental glass-ceramic customization. You can contact our sales team to discuss your specific requirements and custom solutions.
Q6: How can I get the ERADENT dental glass-ceramic price list for distributors?
A6: Please visit our official website or contact us via WhatsApp. Our sales team will provide you with a detailed dental glass-ceramic price list for distributors and a personalized quote.